Basics
Hydrolysis Mechanism and Countermeasures
Hydrolysis is a phenomenon in which materials that contain ester bonds in their molecules—such as polycarbonate and polyester resins—react with water and the bonded sites undergo molecular chain scission.
This degradation can cause variations in flowability, reduced strength, and molding defects such as silver streaks, bubbles, drooling, and stringing.
Because Iupizeta EP, a specialty polycarbonate material, is also susceptible to hydrolysis even with minisicule traces of moisture, proper drying with appropriate equipment and conditions is extremely important.
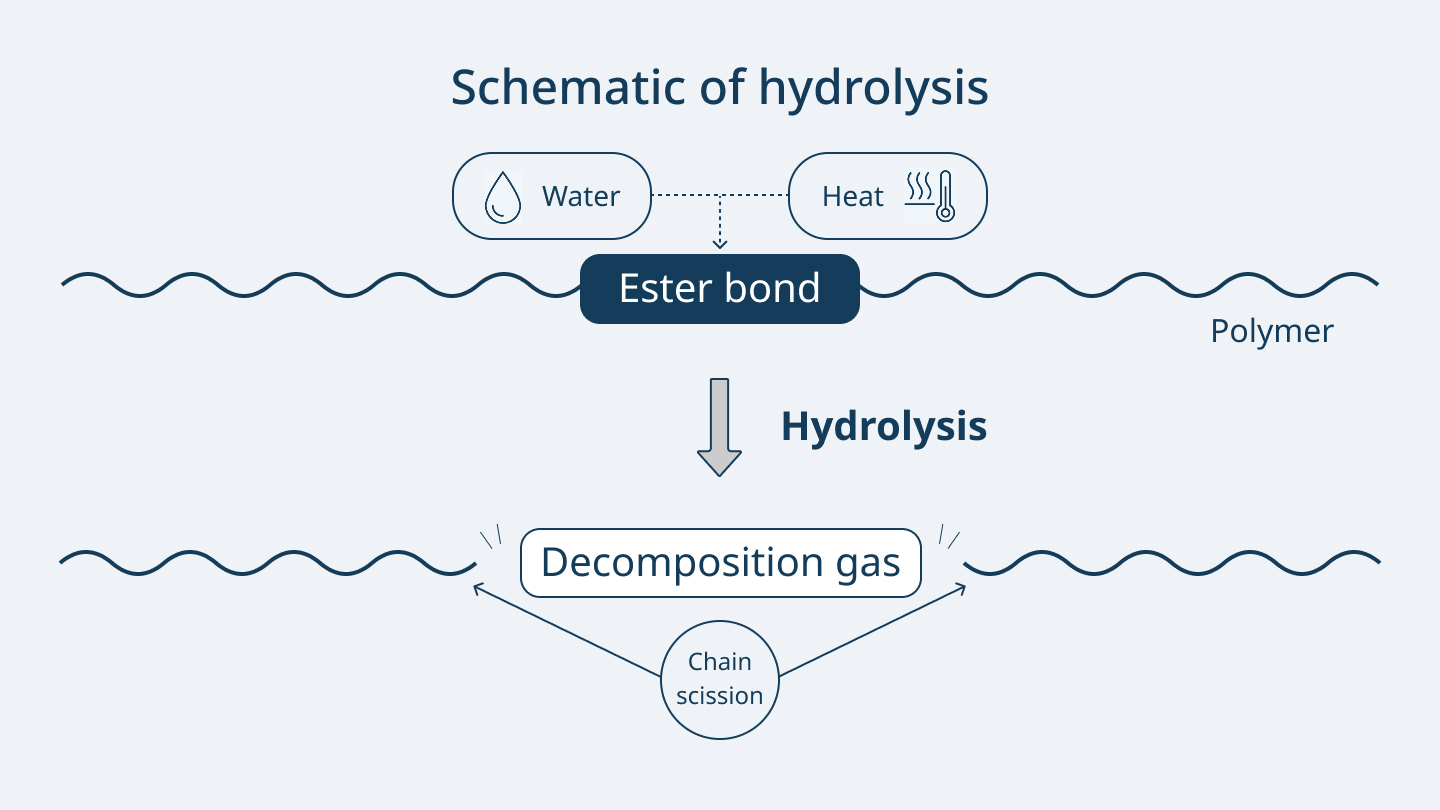

※This article is written with the use of Iupizeta EP in mind and does not apply to all plastics.





